Rome – Worldwide commerce of meals and agricultural merchandise has grown robustly in current a long time and makes very important contributions to meals and nutrient variety, availability and affordability all over the world, a brand new report from the Meals and Agriculture Group of the United Nations (FAO) reveals.
On the similar time, commerce can, in some contexts, be an accelerator of unwelcome adjustments in dietary patterns, boosting consumption of meals with low dietary worth, and excessive in fat, sugar and/or salt. This highlights the necessity to develop commerce insurance policies which can be coherent with nationwide vitamin and public well being goals, in accordance with The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO) 2024.
“The enlargement of worldwide meals commerce has been influenced by multilateral commerce guidelines which have formed a freer, fairer, and extra predictable commerce setting, which, together with an growing variety of regional commerce agreements, has promoted commerce in meals,” mentioned FAO Director-Normal QU Dongyu.
The report, entitled Commerce and Diet: Coverage Coherence for Wholesome Diets, emphasizes the necessity to strengthen coverage coherence between commerce and vitamin sectors to guarantee that commerce doesn’t undermine eating regimen high quality and contribute to rising charges of weight problems and obese.
It additionally notes that hyperlinks between commerce and vitamin are intricate and heterogeneous, and warrant nearer consideration. As incomes rise, a welcome impact of improvement, import demand for ultra-processed meals rises even quicker, underscoring the utility of enabling coverage makers to think about the position of vitamin.
Commerce is prime for meals safety and vitamin
Worldwide commerce on common doubles the range of meals accessible in a rustic catalyzing extra numerous meals provide and diets that are a internet plus for vitamin objectives, particularly in nations with much less numerous geographies comparable to Kiribati or Norway. Dietary variety is vital for the adequacy of micronutrient provide.
Commerce-driven variety additionally results in a extra equal distribution of vitamins comparable to vitamin C, calcium, and zinc, which is vital on condition that the home meals manufacturing of many nations doesn’t meet the nutrient necessities of their populations. SOCO 2024 presents ample knowledge on how world flows of crucial vitamins fill such gaps.
Meals costs are typically decrease in nations which can be open to commerce. This discovering applies throughout the board together with staples, contemporary meals, and processed meals.
Though meals commerce is a cornerstone of meals safety, in some contexts it might produce negative effects, specifically weight problems, a topic that SOCO 2024 investigates in depth. The worldwide prevalence of undernourishment, FAO’s anchor metric for starvation, declined to 9.2 p.c in 2022 from 12.7 p.c in 2000. Over that interval, the worldwide prevalence of weight problems within the grownup inhabitants elevated from 8.7 p.c to fifteen.8 p.c.
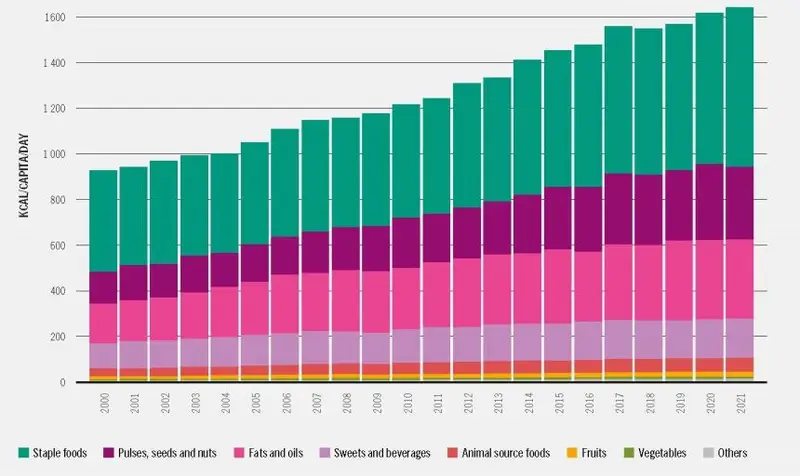
Commerce has elevated in all meals classes, and in any respect processing ranges, since 2000. Staple meals account for the most important share of energy traded, however their share is declining whereas these of fat and oils, pulses, seeds and nuts and animal-source meals is rising.
Some key findings
Practically 5 000 trillion kilocalories have been traded in 2021, greater than double the dietary vitality traded in 2000. Day by day per capita meals commerce elevated to1 640 kcal from 930 over that point.
A ten p.c improve in revenue leads to an 11 p.c improve within the demand for imports of ultra-processed meals and a 7 p.c improve within the demand for imports of unprocessed and minimally processed meals.
Between 1961 and 2021, the worldwide per capita common dietary vitality accessible for human consumption elevated by 35 p.c, from 2 200 to 2980 energy per particular person per day. In 1961, staple meals accounted for 57.4 p.c and declined to 48.4 p.c. The share of animal supply meals grew from 12.2 p.c to fifteen.1 p.c and that of fat and oils elevated from 8.4 to 12.7 p.c.
Per capita commerce in vitamin C and calcium from meals elevated by virtually 90 p.c between 2000 and 2021.
In 2020, nations produced a median of 120 completely different meals objects, whereas commerce lifted the variety of meals objects accessible to a median of 225, with important progress recorded previously decade.
Extremely-processed meals accounted for 7 p.c of worldwide traded energy, and 12 p.c of meals imports in high-income nations in 2021. In financial phrases, the worth of imported ultra-processed meals was a lot bigger than their caloric share.
Growing funding and innovation in meals processing sectors means extra processed meals can be found regionally and distributed extensively by means of the proliferation of supermarkets. SOCO presents proof of how the tempo of dietary transformation in low- and middle-income nations linked to this, and to fast urbanization, considerably outpaces such adjustments in what at the moment are high-income nations.
Commerce governance
Whereas commerce liberalization has quite a few advantages for meals safety, questions linger about whether or not it’s conducive to wholesome diets. An evaluation for SOCO 2024 utilizing FAO’s Price and Affordability of a Wholesome Weight-reduction plan indicator discovered that increased import tariffs are related to increased meals costs no matter the wholesome qualities of the meals, indicating that, basically, commerce openness doesn’t have a disproportionate impact on high-energy low-nutrition meals.
The SOCO 2024 report provides concerns of the position of recent regional commerce agreements, which transcend market entry and tariff reductions and focus extra on harmonizing non-tariff measures and home laws overlaying requirements associated to components, pesticide residues and labelling necessities.
It finds some proof that regional commerce agreements with a excessive variety of sanitary and phytosanitary provisions have a tendency to extend imports of ultra-processed meals, that are additionally notably extra attentive to revenue adjustments.
The report additionally evaluations case research of efforts to combine vitamin objectives into commerce insurance policies and the way these can adjust to or run afoul of multilateral guidelines.